The Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive came into force on January 5th 2023 mandating companies to include sustainability reporting as part of their annual financial reports. Companies will have to apply the new rules for the first time in their 2024 financial year reports. The directive applies to both large and listed companies, requiring them to disclose relevant environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data to stakeholders. Although smaller entities might benefit from certain exemptions, the CSRD casts a broad net to ensure greater transparency across various industries.
Corporate sustainability reporting plays a crucial role in driving sustainable practices and fostering accountability among businesses. The introduction of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) marks a significant development in the field, taking the commitment to sustainability reporting to new heights.
The CSRD is a directive aimed at enhancing sustainability reporting among companies operating within the European Union (EU). It seeks to improve the quality, transparency, and comparability of sustainability information, building upon existing reporting frameworks and regulations. The EU’s leadership in this initiative carries global implications, inspiring companies worldwide to adopt more robust sustainability reporting practices.
Compared to previous reporting standards, the CSRD introduces significant changes. It expands the range of mandatory sustainability reporting requirements, encompassing a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) and specific disclosure topics. By doing so, the CSRD aims to foster consistency, comparability, and reliability in sustainability reporting, enabling stakeholders to make more informed decisions.
The implementation will affect companies of all sizes and industries, driving them to adopt more comprehensive sustainability reporting practices. Businesses can expect numerous benefits, including improved reputation, enhanced stakeholder engagement, and increased access to capital from investors prioritising sustainability. However, the transition to CSRD compliance may pose challenges.
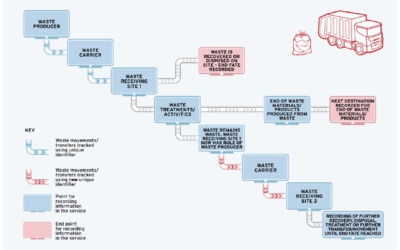
One crucial area impacted by the CSRD is waste and materials management within companies. Sustainability reporting will now necessitate a comprehensive understanding of waste generation, handling, and disposal practices. The CSRD will influence waste management in the following ways:
- Data Collection and Reporting Requirements: Companies will be required to collect and report data on waste generation, recycling, and disposal to meet sustainability reporting standards. This will necessitate streamlining data collection processes and ensuring data accuracy.
- Promoting Circular Economy Principles: The CSRD will act as a catalyst for companies to adopt circular economy principles. Businesses will be encouraged to reduce waste generation, promote product recycling and reuse, and extend product lifecycles.
- Enhanced Waste Reduction Strategies: The CSRD will push companies to develop more robust waste reduction strategies, leading to reduced waste volumes, increased recycling rates, and minimized environmental impact.
- Supply Chain Sustainability: Companies will need to track waste and materials across their entire supply chain to address the environmental impact of sourcing and manufacturing processes.
- Encouraging Resource Efficiency: The CSRD will incentivise companies to optimise material usage, minimise waste, and adopt resource-efficient practices to improve their overall sustainability performance.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): The CSRD may introduce or reinforce EPR measures, making companies responsible for managing their products and packaging waste, leading to greater emphasis on eco-design and sustainable product packaging.
- Innovation in Waste Management: The CSRD will likely spur increased investment in waste management technologies and infrastructure as companies seek to comply with the directive’s requirements.
- Engaging Stakeholders: Collaboration with stakeholders, including waste management providers and consumers, will be crucial for managing waste and materials sustainably.
- Environmental Benefits: Improved waste and materials management will result in reduced greenhouse gas emissions, conservation of natural resources, and decreased landfill waste, benefiting the environment.
- Driving Cultural Change: The CSRD can foster a cultural shift within organisations, promoting a deeper commitment to sustainable practices and waste reduction as a core business value.
The advancements in the CSRD will require technology to play a significant role. Software can help facilitate the collection, analysis, and reporting of sustainability data while digital reporting platforms and tools will streamline the reporting process and ensure data accuracy.
The CSRD will also provide investors with more comprehensive and reliable sustainability information, enabling better-informed investment decisions and the integration of ESG factors into investment strategies. And with the increased regulatory measures and penalties to ensure companies’ compliance, audit processes will verify the accuracy and reliability of sustainability reports.
There are of course challenges of the CSRD, including data collection and verification difficulties and the importance of setting realistic targets and goals to achieve sustainable development. The directive will continually evolve to address emerging issues and developments.
Ultimately, the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) marks a significant milestone in advancing corporate sustainability practices. By promoting transparency and accountability in sustainability reporting, the CSRD will have far-reaching impacts on waste and materials management, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and responsible future. Businesses, regulators, and stakeholders must collaborate to ensure successful implementation and achievement of sustainability goals through the CSRD.
ISB Global supports the advancement of sustainability reporting through Waste & Recycling One (WR1), an integrated waste & recycling software solution that delivers instant control and complete visibility across waste management and recycling operations. It allows you to know where materials are, how much you have and what they are worth with reporting, analytics and intelligence on all aspects of collection and material recycling operations, in real-time.
To learn more about a solution that can give you complete, accurate, real-time data and one version of the truth, contact the team today.